Other Projects
Life Cycling System

The system mainly developed for study the reliability and ageing effect of the pressure transducers which will going to use on aerospace applications. The Pressure cycle test set up comprises of two solenoid valves – one for pressurizing and the other for depressurizing, an electronic square wave oscillator with transistor relay drive circuit for controlling the “ON” and “OFF” timings of the solenoid valves, power supply for exciting the electronics and solenoid valve, and pneumatic interconnecting adaptors.
During the test, for recording the output data of the pressure transducer, data acquisition system is also incorporated in the set up.

Peristatic pump for drug delivery system
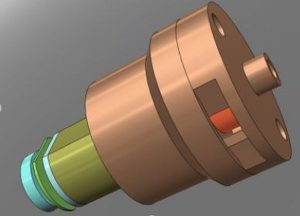
Micropump technology has emerged as a critical research area for the biological analysis, electronic component liquid cooling, medicine, space exploration, thermal management, etc. The pumping mechanism of the micropump will depend on their targeted applications. Mainly, three types of actuating mechanism based micropumps have been reported: (I) mechanical displacement, (II) electro-kinetic, and (III) magneto-kinetic. In present study, a mechanical displacement principle has been adopted. Peristalsis mechanism based pumps are called as peristaltic pumps. These peristaltic pumps often consist of rotating rollers to squeeze the flexible tube containing a fluid. The squeezing action of the peristaltic pump has been created by various means such as motor driven rollers, magnetic balls, Shape Memory Alloy (SMA) actuation, and Lead Zirconate Titanate (PZT). In the present study, a geared DC-motor driven roller/cam was used to squeeze the silicone tube to obtain the pumping action. The aim of this work is to design and develop a peristaltic micropump suitable for drug delivery application. In particular, development of an insulin delivery pump for diabetic people. While designing a micropump for drug delivery or insulin delivery application, one has to consider the following important aspects.
Fail-safe operation—in case of motor failure the pump should block the flow of fluid positively.
- Compactness and light weight to facilitate ease of wearing.
- Low energy consumption, as the system is battery operated and the battery should last till the entire insulin in the source cartridge is dispensed.
- Ease of programmability of flow rate and volume.
- User friendly operation, to provide ease of loading and unloading of the catheter and insulin cartridge without contaminating the drug.
- The pump should generate enough pressure to pump the drug against the blood pressure.
- Fail-safe operation—in case of motor failure the pump should block the flow of fluid positively.
Power device GaN package

POWER semiconductor device packaging is in many ways similar to that of IC packaging. It provides mechanical support to the fragile chip, electrical interconnections, heat dissipation paths, and protection from the environment. However, there are important differences between the two that are dictated by the functions of the power device. For example, the number of interconnections necessary is substantially less than that of a microprocessor. In a power MOSFET or insulated gate bipolar transistor (IGBT), a minimum of three interconnections are necessary (drain, source, and gate). Power devices usually handle much larger currents and voltages such that they require larger interconnections and more efficient thermal management. Such seemingly minor and simple differences may not be that easy to implement in real package structures because of constraints on the physical properties of the device and package component materials and the thermomechanical issues such as coefficient of thermal expansion (CTE) mismatches that can adversely affect the performance and reliability of the package or module.


IoT Module

Internet of Things (IoT), which is transforming almost every industry, including retail. Devices with smart sensors are capable of collecting and exchanging observational and transactional data with each other, making them seamlessly interconnected. The data gathered from IoT can be utilized to provide insights, trigger actions and control outcomes all in real time with or without any human intervention.
There are three stage in the development process First one will be the design of the sensor node, where all the sensor required for the monitoring parameter are put together with in an embedded system having a Wi-Fi transverse. The second will the Power Management. The third will be the Designing the architecture for Server. That provides functionality for other programs or devices, called “clients”(Sensor node). This architecture is called the client–server model, and a single overall computation is distributed across multiple processes or devices.
Results of IoT Module
Microthrusters

Microthrusters are an application of MEMS technology to the field of aerospace. These are propulsion systems that require no elaborate pump, valves or piping systems. The work currently is centered around developing Microthrusters that are capable of operating in a continuous mode. From solid propellant combustion to decomposition of a liquid mono-propellant, different techniques have been explored to obtain thrusts in the range of a milliNewton sans compromising on the specific impulse
Body Conduction

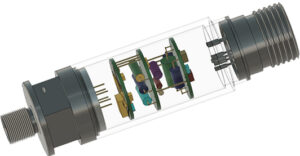
Design and Development of Gas Sensors and Transmitters to replace imported units

This Project is for Leak Detection of Various Gases used in the Industry. The Transmitter Monitors Gases such as O2, NO2, H2, N2H4 and Transmits 4-20ma on a 2 wire loop to indicate the Leak concentration of the Gases. The unit is Palm Sized(130LX80 WX55D mm) and has a intelligent Algorithm which compensates the RH% variation and updates the Minimum threshold of Gas Concentration.
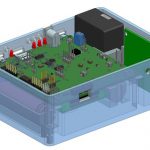
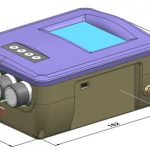
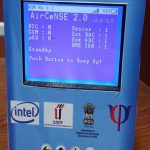
Realtime Air Quality Monitoring System
The Realtime Airquality Monitoring System updates on a Real Time basis the Data of CO, CO2, SO2, NO2 Sensors along with Ambient RH & Temp. The purpose of this is to demonstrate the Nanosensors developed and Fabricated at CeNSE-IISc. Along with Machine Learning and Data Analytics it gives Real Trend of Pollutants in the Environment. The Cloud Hosted Data Base updates all 6 Sensors Data once in ~50secs.


| Model | Air CeNSE 2.0 |
| Detectable Gases | CO,NO2,SO2,CO2 |
| Max Detectable Gas Concentration range (xx/m3) | CO-mg/m3 | CO2-ppm | NO2(ug/m3) | SO2(ug/m3) 10 | 1000 | 100 | 100 |
| Detectable Particle size | 2.5µm – 10µm |
| Humidity Sensor Range | 40%RH to 100%RH |
| Temperature Sensor Range | 25°C to 85°C |
| Noise Max Level | 120dB |
| Pressure Sensor Range | 5psi to 16 psi |
| Supply Voltage | DC 5V |
| Storage Temperature | 25°C to 85°C |
| Battery Backup-Continuous | 4 Hr |
| Dimensions-TBD | ~110(W) | ~50(H) | ~165(L) |
| Weight-TBD | ~500gm |
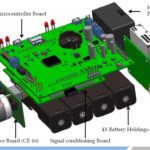
The Design of AQM is based on STM32F411 Arm Cortex M3 Microcontroller and has a Microcontroller board which has a Display Interface, Battery Charging Circuit, GSM Interface, LCD display, Keypad, SD Card Interface and samples the 6 Sensors Data with ADC and Mux Configuration.
The Final unit is connected to Cloud to update all 6 Sensors Data on a Grafana Data base with 1 minute update on a real time basis.
There is a Signal Conditioning Board with Transconductance Amplifier to program the 4 sensor and heater Voltages . In addition a RH/ Temperature Sensor measures the ambient environment condition.
The Firmware is written for boot up and for sensor, heater ramp up happens and reads the sensor current. The values of Each Sensor converted units of levels are done using an appropriate Algorithm.